Shrinking
Shrinking
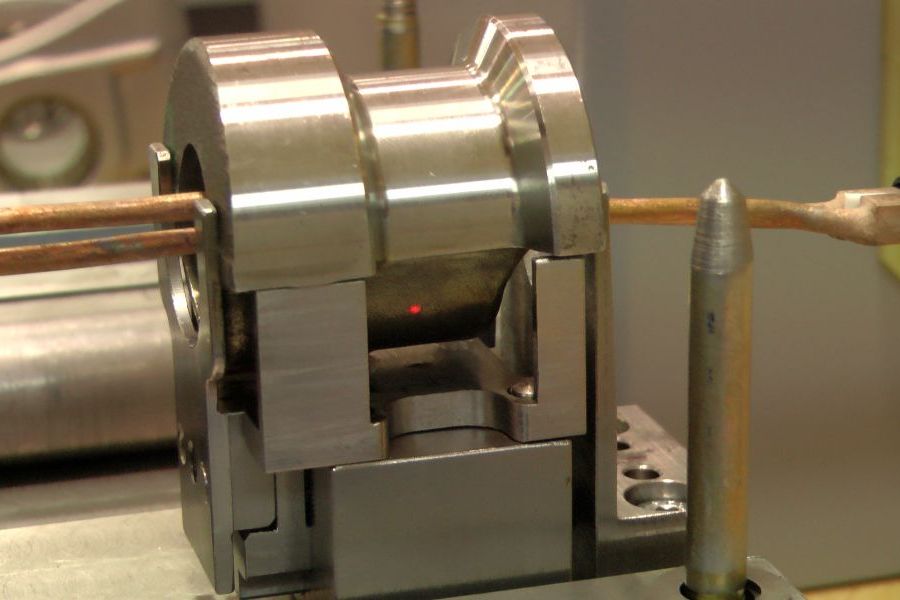
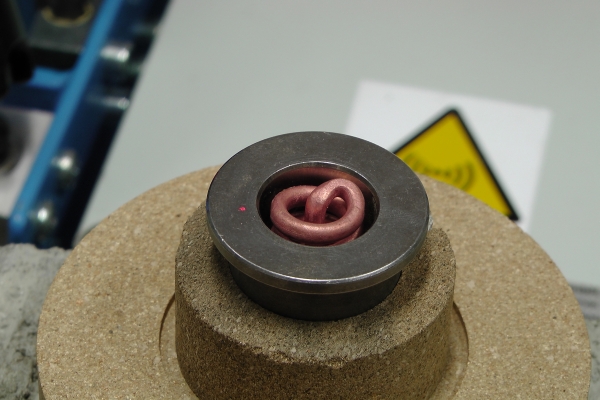
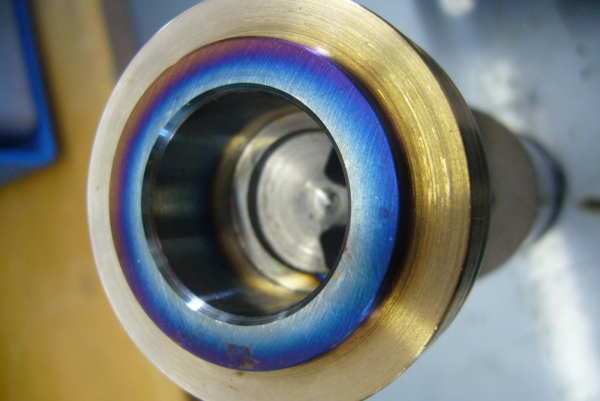
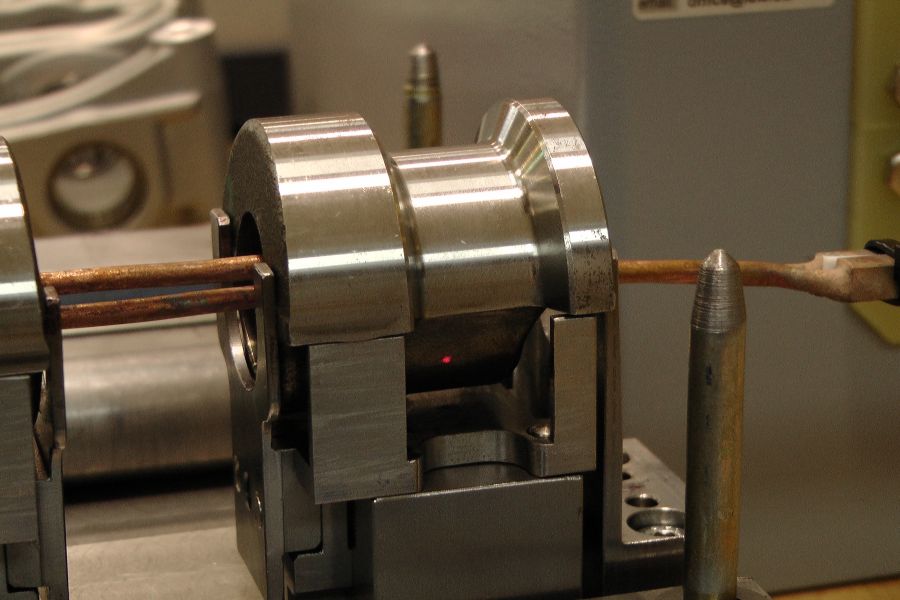
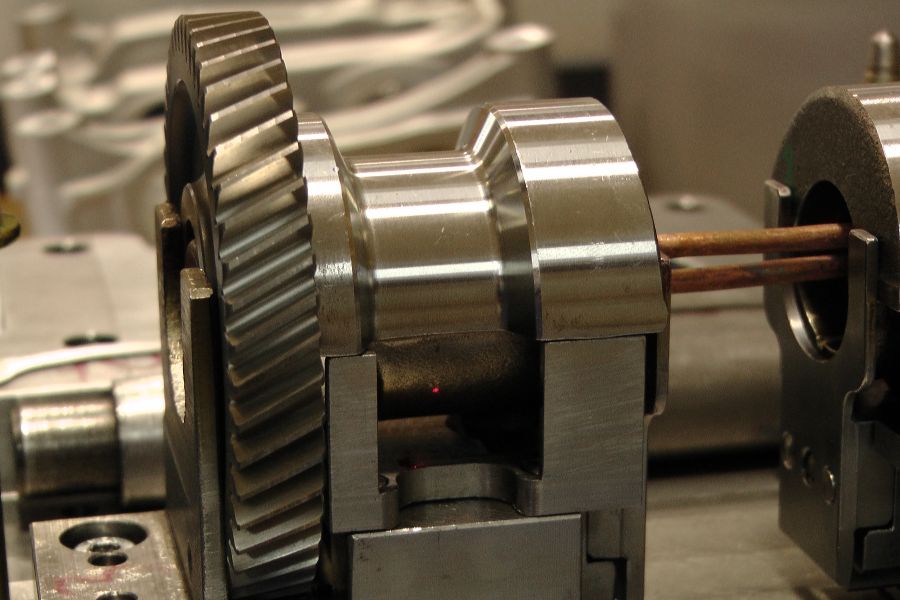
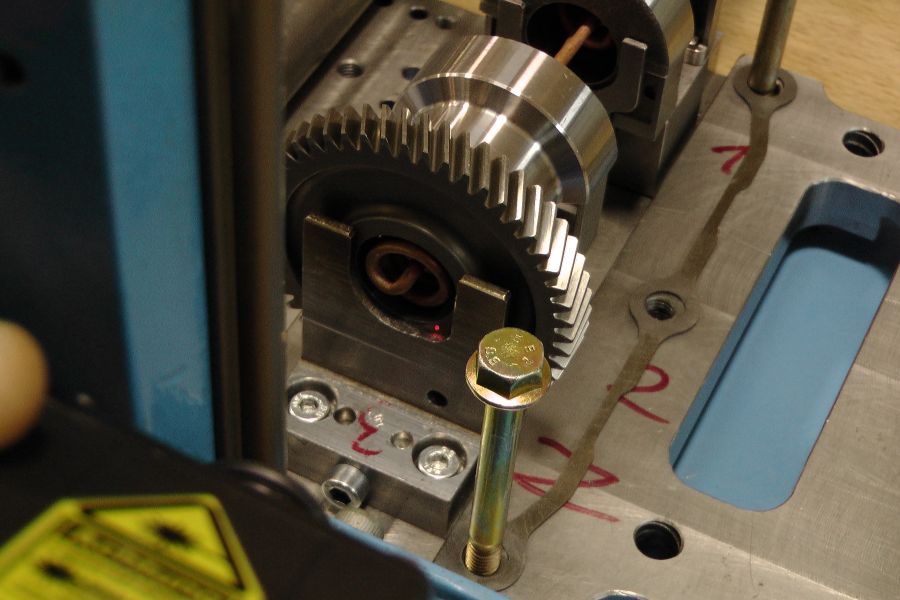
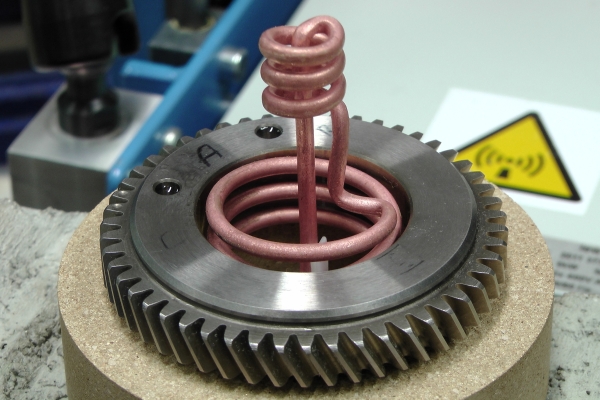
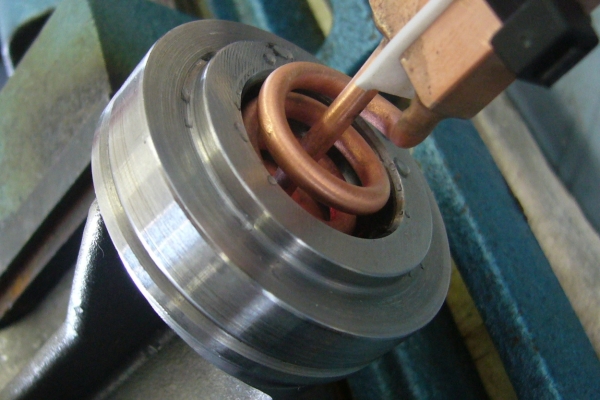
The shrink fitting of two workpieces (e.g. gearwheel, unbalanced mass, shaft, etc.) creates a friction-locked connection. This method is based on the principle of the thermal expansion of metals.
For example, when a gearwheel is heated to a temperature at which its inner bore expands enough to be easily placed onto a shaft, and then cooled, the bore contracts to form a secure, friction-locked fit with the shaft.
At room temperature, these components could only be joined with considerable force, which may result in damage to the fitting surface (e.g. scoring). Using the induction heating method allows for a faster, safer, and more precise assembly process.